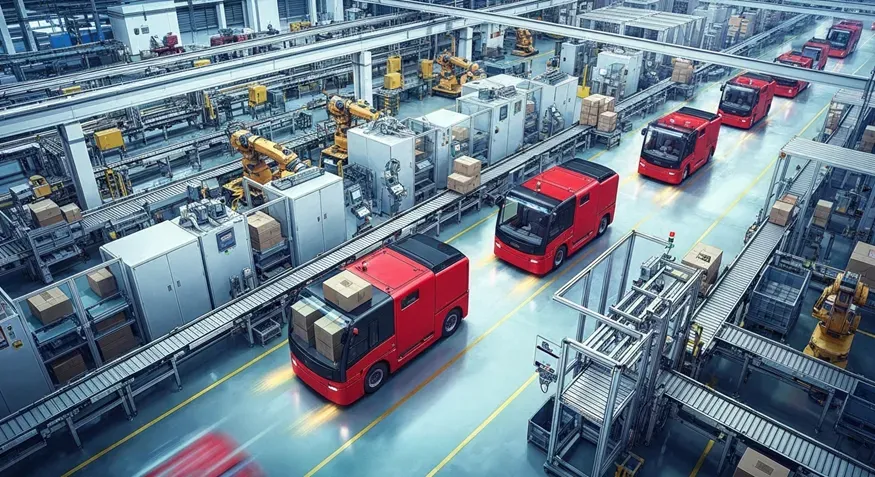
PLC programming languages are essential tools for controlling industrial automation processes. Common languages include Ladder Logic, which resembles electrical relay diagrams and is intuitive for many engineers; Function Block Diagrams (FBD), enabling modular and structured programming; and Structured Text (ST), providing a high-level language for complex algorithms and mathematical operations. Each language serves specific purposes and allows programmers to design efficient and reliable control strategies tailored to diverse industrial applications.
PLCs
What is PLC?
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a specialized digital computer used in industrial automation and control systems. It serves as the brain of machinery and processes, executing programmed instructions to control various electromechanical operations. PLC and HMI Programming are designed to withstand harsh industrial environments, offering high reliability and robustness. They are programmed using ladder logic or other languages to interface with sensors, actuators, and other devices, enabling precise and efficient control of automated processes.
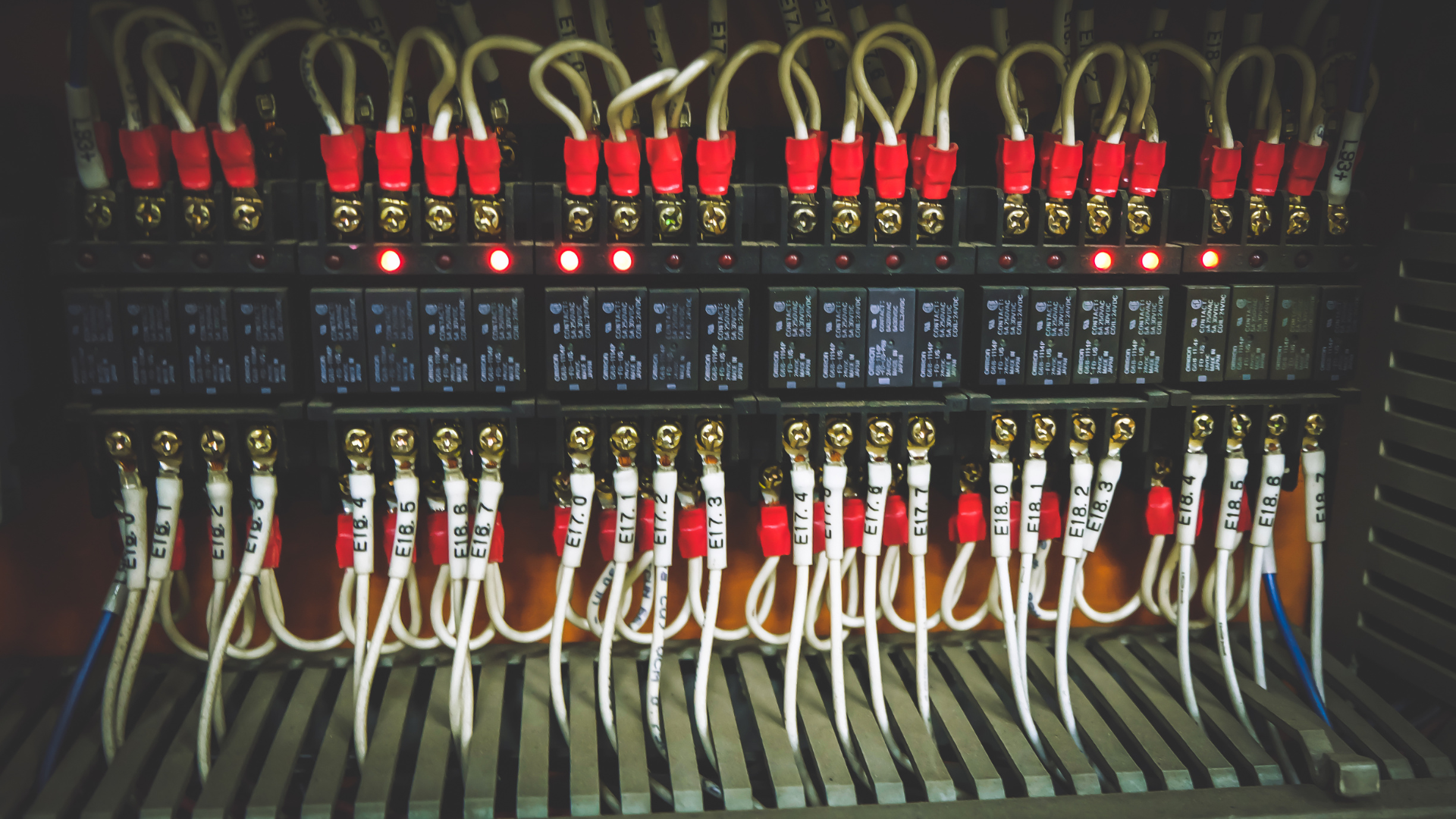
PLC Brands
There are several prominent brands in the field of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), each offering unique features and capabilities. Siemens, a well-known brand, provides a comprehensive range of PLCs suitable for various industrial applications, known for their reliability and versatility. Allen-Bradley, another leading brand, offers PLCs renowned for their robustness and compatibility with a wide array of automation systems. Schneider Electric is also a notable player in the PLC market, providing innovative solutions tailored to specific industrial needs with a focus on efficiency and scalability. These brands, along with others like Mitsubishi Electric and Omron, continue to drive advancements in PLC technology, empowering industries with enhanced automation capabilities.
PLC Programming Languages
Components of PLC
The components of a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) consist of three primary elements: input modules, CPU, and output modules. Input modules facilitate the connection of sensors and switches to the PLC, converting physical signals into digital data that the CPU can process. The CPU, often referred to as the brain of the PLC, executes programmed instructions and coordinates the operation of the input and output modules to control industrial processes effectively. Output modules interface with actuators and other devices, converting digital signals from the CPU into physical actions, thus completing the feedback loop of the automation system.
PLCs Login
PLCs typically do not have a traditional "log in" process like computers or networks. Instead, PLCs are configured and programmed by engineers and technicians using specialized software and hardware interfaces. Access to PLC programming and configuration is usually controlled through physical or digital security measures implemented by the organization to prevent unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of industrial automation systems.
Types of PLC
Advantages of PLC
The advantages of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) lie in their ability to automate industrial processes efficiently and reliably. PLCs offer flexibility in programming, allowing for easy modification and adaptation to changing production needs without significant downtime. Additionally, PLCs are ruggedized for harsh industrial environments, ensuring durability and consistent operation, while their modular design enables scalability, making them suitable for applications of varying sizes and complexities.
MyApps PLCs Login
"MyApps PLCs Login" refers to a specific system or application for accessing Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). Typically, such login systems would provide authorized personnel with secure access to PLC programming and configuration interfaces. These login systems may incorporate authentication measures such as usernames, passwords, and possibly additional security layers to prevent unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of industrial automation systems.
What is PLC in Electrical?
In electrical engineering, PLC stands for Programmable Logic Controller, a specialized digital computer used to control electromechanical processes. PLCs play a crucial role in automating various electrical systems and machinery in industrial settings. By processing input signals from sensors and executing programmed instructions, PLCs can regulate the operation of motors, valves, and other electrical components, thereby optimizing efficiency and enhancing safety in electrical applications.
PLCs Clever Login
"PLCs Clever Login" suggests a specialized login system for accessing Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) that might incorporate advanced authentication methods or features. This login system could potentially utilize biometric authentication, multi-factor authentication, or other intelligent security measures to ensure only authorized personnel can access the PLC programming and configuration interfaces. By implementing such a "clever" login system, organizations can enhance security and protect industrial automation systems from unauthorized access or tampering. This transformation occurs across industries, offering insights into the capabilities and challenges of advanced industrial systems.
My Apps School Login
PLC School Login serves as the gateway for students and professionals to dive into the realm of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). Through this platform, users gain access to a wealth of educational resources, including tutorials, simulation software, and instructional videos, tailored to enhance their understanding and proficiency in industrial automation. With a simple login, learners embark on a journey of exploration and skill development, unlocking the potential of PLC technology in various industrial applications.
PLC Diagram
A PLC diagram visually represents the logic and control processes programmed within a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC). Typically created using software tools such as ladder logic editors, PLC diagrams illustrate the flow of signals and decision-making steps involved in automating industrial processes. By providing a clear and intuitive depiction of the control logic, PLC diagrams aid engineers and technicians in designing, troubleshooting, and optimizing PLC-based systems for efficient operation.
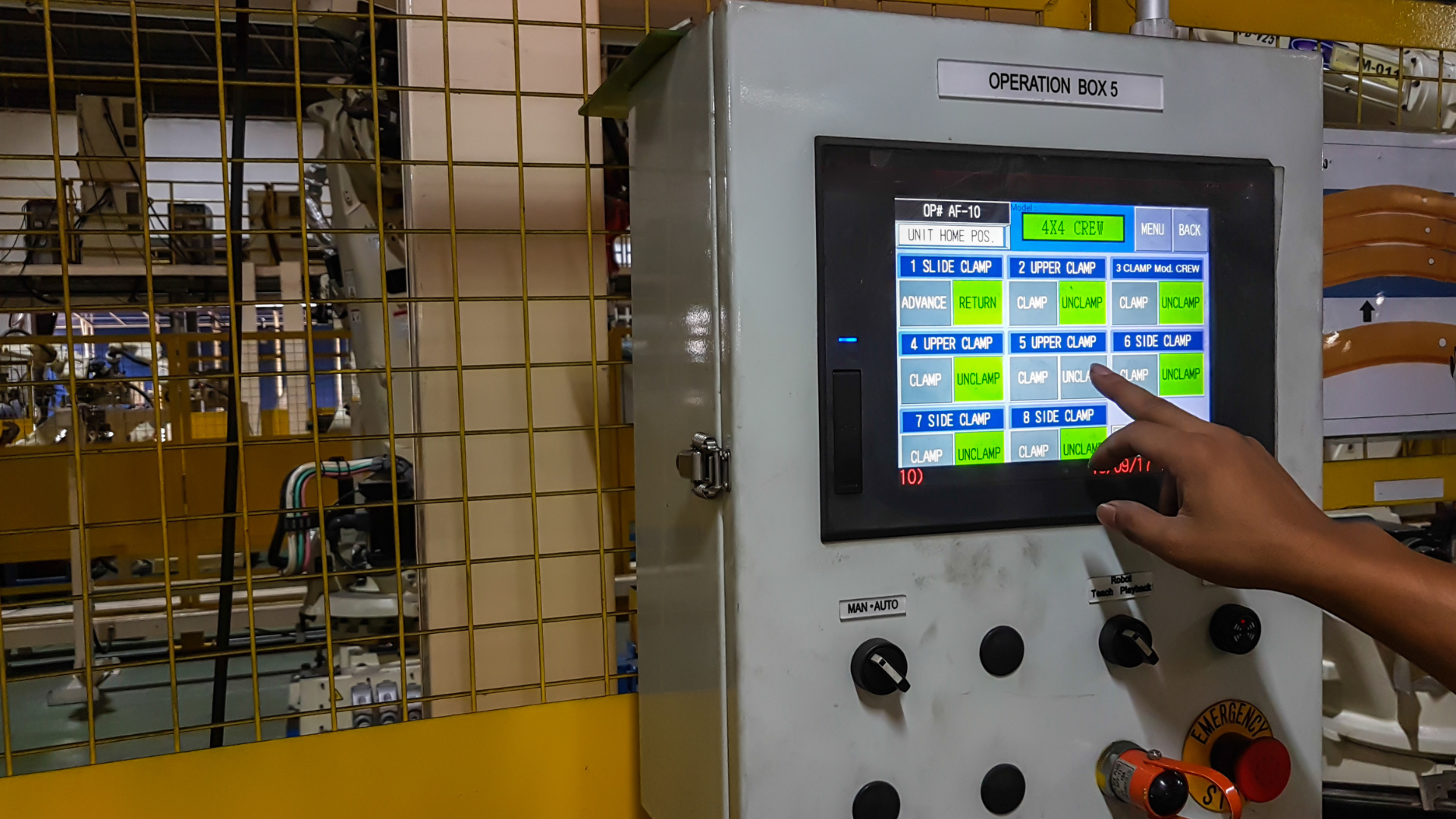

PLC Full Form
The full form of PLC stands for Programmable Logic Controller, a pivotal component in industrial automation. Programmable Logic Controllers are specialized digital computers designed to control electromechanical processes with precision and reliability. From manufacturing assembly lines to robotic systems, PLCs play a critical role in optimizing efficiency and ensuring the seamless operation of complex industrial systems.
PLC Working Principle
The working principle of a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) revolves around processing inputs, executing programmed logic, and generating outputs to control industrial processes. PLCs continuously scan input signals from sensors, switches, and other devices to monitor the state of the system. Based on predefined logic programmed by engineers, PLCs make real-time decisions to activate or deactivate outputs, effectively regulating machinery and automating industrial operations with precision and reliability.
PLC Programming Examples
PLC programming examples showcase the versatility and practical applications of programmable logic controllers in industrial automation. These examples often include scenarios such as controlling conveyor belts, regulating temperatures in industrial ovens, or managing assembly line operations. By studying and implementing PLC programming examples, engineers and technicians gain insights into the logic and methodologies behind designing efficient control strategies for diverse industrial processes.






