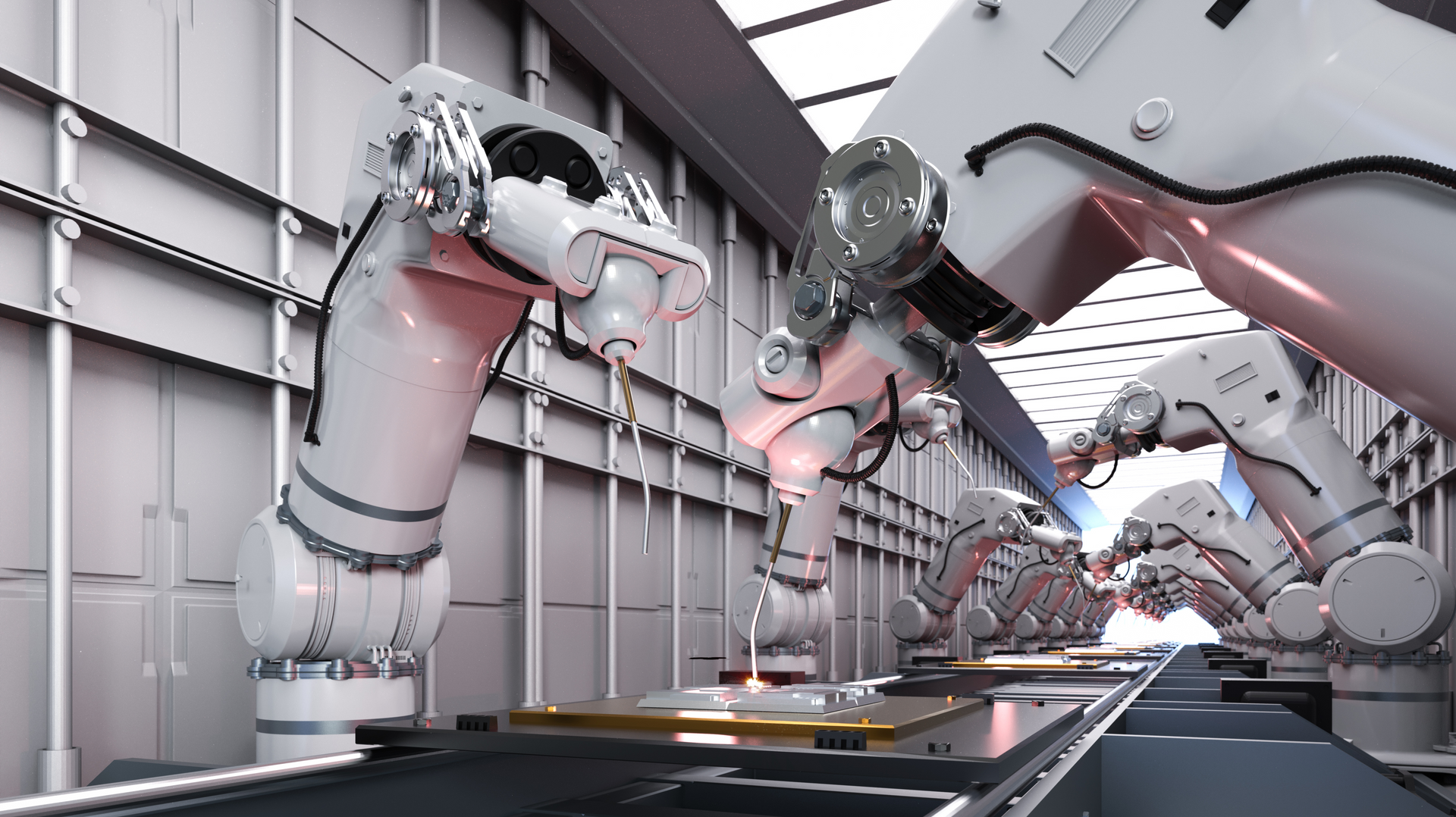
What are the 4 Types of Automation
The four types of automation, often discussed in the context of industrial and business processes, are:
- Fixed Automation (Hard Automation): This type of automation is characterized by production equipment that is configured for mass production. It's designed to perform a specific task with high efficiency and a fixed sequence of operations, typically found in manufacturing environments with high production volumes. The equipment is generally expensive, with a high initial investment, but it leads to lower production costs per unit.
- Programmable Automation: Suitable for batch production, programmable automation allows for reprogramming of machines to accommodate different product configurations. This flexibility is ideal for manufacturing environments where the product design changes periodically. Though it offers more versatility than fixed automation, it requires downtime for reprogramming and setup changes.
- Flexible Automation (Soft Automation): This automation type provides an even higher level of flexibility. Machines can be quickly switched over to produce different products without significant downtime for reprogramming or setup changes. It's particularly effective in environments where products are made in small to medium volumes and designs change frequently.
- Integrated Automation: This represents the most advanced form of automation, where entire production processes or even entire factories are automated. It involves the integration of various automated systems, including production, material handling, and quality control, all interconnected and controlled via advanced information technology systems. This level of automation is at the heart of what's often referred to as a "smart factory" in the context of Industry 4.0.
Understanding these types of automation is crucial for businesses and industries as they choose the right automation strategies to improve efficiency, productivity, and adaptability in their operations.
Fixed automation
Fixed automation, also known as hard automation, refers to a manufacturing process that is designed to produce a specific type of product or component in high volumes with very little variability. The machinery and equipment are configured with a set sequence of operations, tailored to maximize efficiency and output for that particular product. This type of automation is characterized by its high initial investment and inflexibility; changing the system to produce different items can be costly and time-consuming. However, fixed automation systems offer significant advantages in terms of speed, cost per unit, and consistency, making them ideal for large-scale production runs of a single product type.
Types of Automation
Automation can be broadly categorized into several types, each suited for different applications and industries. Fixed automation, or hard automation, involves pre-programmed sequences for high-volume production with minimal variability. Programmable automation allows for flexibility where equipment can be reconfigured for different tasks or products, ideal for batch production. Flexible automation, or soft automation, offers a high degree of adaptability, enabling quick changes between tasks without significant downtime, suitable for varying production needs. Lastly, integrated automation represents the pinnacle of automation, where entire systems or factories are interconnected and controlled automatically, often seen in smart manufacturing environments.
Automation Categories
Automation can be categorized into various types based on its application, flexibility, and level of integration. Here are some key categories:
- Industrial Automation: This involves using control systems and machinery to automate industrial processes, reducing human intervention. It includes the use of robots, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and other machinery in manufacturing, packaging, and quality control.
- Office or Business Process Automation: This type of automation streamlines administrative and office tasks, such as data entry, scheduling, and document management, using software tools and applications to increase efficiency and reduce errors.
- Home Automation: Also known as domotics, this category includes the automation of household activities and appliances. It often involves controlling lighting, climate, entertainment systems, and appliances to improve comfort, convenience, and energy efficiency.
- IT Automation: This encompasses the use of software to create repeatable instructions and processes to replace or reduce human interaction with IT systems. It includes tasks like network configuration, system management, and deploying software updates.
Each category of automation leverages technology to improve efficiency, accuracy, and consistency in its respective domain, contributing to enhanced productivity and reduced operational costs.
Japanese Automation Companies
Advantages of Automation
Automation significantly enhances efficiency, enabling machines to perform tasks at a faster rate and with greater consistency than human workers. It leads to substantial cost savings by reducing labor expenses and minimizing errors and waste in production processes. Automation also improves workplace safety by taking over dangerous tasks and provides around-the-clock productivity without the constraints of human work schedules. Additionally, it facilitates precision and quality control in manufacturing, ensuring consistent and reliable output.
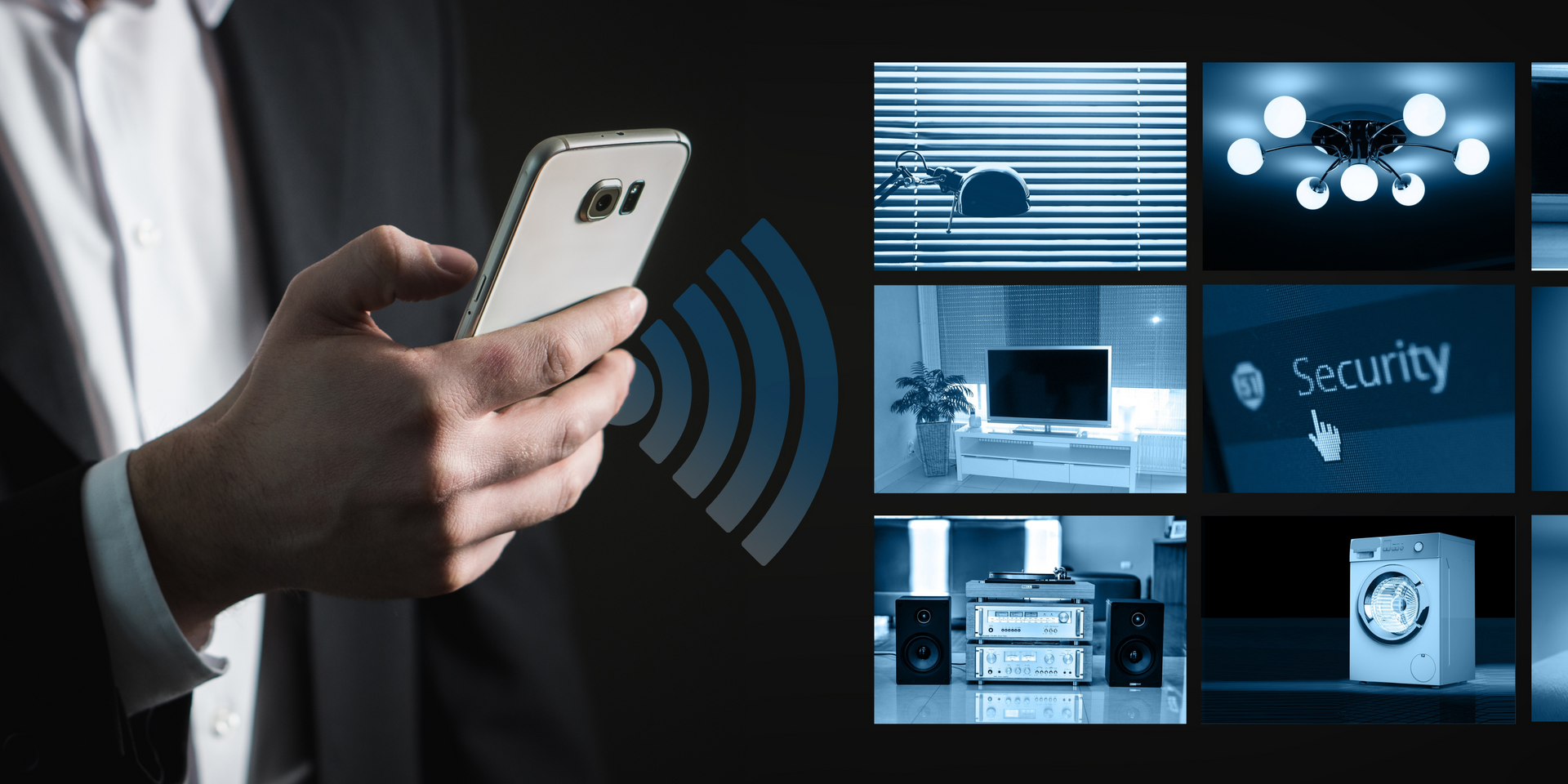
Home Automation
Home automation, also known as domotics, refers to the use of smart devices and systems within a residence to provide convenience, comfort, energy efficiency, and security. Through home automation, various household functions such as lighting, heating, air conditioning, entertainment systems, and security cameras can be controlled remotely via smartphones or other networked devices. This technology enables homeowners to schedule operations, monitor real-time status, and automate responses to certain events, enhancing the living environment and potentially reducing energy costs. Home automation not only adds to the convenience and luxury of modern living but also contributes to smarter, more efficient home management.
Top Software Automation Companies
Top software automation companies are revolutionizing how businesses operate, enhancing efficiency and accuracy across various industries. UiPath and Automation Anywhere stand out in the field of robotic process automation (RPA), offering tools that automate routine, rule-based tasks, thereby freeing up human resources for more strategic activities. Another notable company, Blue Prism, provides a digital workforce powered by software robots, helping businesses automate complex, end-to-end operational activities. Additionally, companies like Selenium provide powerful tools for automating browser actions for testing web applications, further exemplifying the diverse applications of software automation in improving business processes and productivity.
Top Industrial Automation Companies in USA
In the USA, top industrial automation companies like Rockwell Automation and Emerson Electric are at the forefront of innovation, providing a wide range of automation solutions that enhance manufacturing efficiency and productivity. Rockwell Automation is renowned for its expertise in industrial automation and information technology, offering advanced control systems, software, and services. Emerson Electric, on the other hand, specializes in process control systems, asset management, and automation services, catering to various industries. Honeywell, another major player, delivers comprehensive automation solutions, including control systems, sensors, and software, across diverse sectors, driving operational excellence and digital transformation. These companies play a pivotal role in advancing industrial automation, contributing significantly to the sector's growth and evolution in the USA.