Industry 5.0 PPT
What is Industry 5.0
Industry 5.0 marks a significant evolution in the industrial landscape, focusing on the symbiotic relationship between humans and machines. This new phase emphasizes personalized production, integrating human creativity with advanced technologies to create bespoke solutions. Unlike its predecessor, Industry 4.0 champions sustainability, advocating for environmentally friendly practices and emphasizing social responsibility. It redefines the role of workers, leveraging technology to enhance their capabilities and improve their working conditions. By balancing technological advancement with human insight, Industry 5.0 aims to forge a more sustainable, innovative, and human-centric industrial future.

Industry 5.0 Principles
Industry 5.0 is anchored in the principle of integrating human intelligence and creativity with advanced technological systems to drive innovation, customization, and sustainability in manufacturing. It prioritizes the synergy between human workers and machines, ensuring that technology complements rather than replaces human skills, thereby enhancing the value of human touch in the production process. Moreover, Industry 5.0 emphasizes a strong commitment to environmental sustainability and social responsibility, advocating for production processes that are not only efficient and personalized but also eco-friendly and ethically sound, ensuring a balanced approach to industrial advancement that benefits society, the economy, and the planet.
Industry 5.0 Examples
Industry 5.0 examples include smart factories where robots and humans work side by side, customizing products to individual preferences while optimizing efficiency and safety. It's seen in businesses that leverage AI and human expertise to innovate and solve complex problems, and in companies that adopt green manufacturing, reducing waste and using sustainable resources. These examples showcase the integration of technology and human ingenuity, focusing on customization, collaboration, and sustainability.
What is Industry 5.0 PDF?
Industry 5.0 PDF
Industry 5.0 PDF would delve into how this next phase prioritizes the integration of human intuition and skills with advanced technological systems to create more personalized, sustainable, and efficient manufacturing processes. The document would likely cover how Industry 5.0 fosters collaboration between humans and machines, emphasizes the importance of creativity and personalization in production, and underlines a commitment to environmental and social responsibility. It would also explore practical examples of Industry 5.0 in action, illustrating how businesses are adapting to these new principles to enhance innovation, improve worker satisfaction, and drive sustainable growth. Such a document serves as a resource for businesses, policymakers, and academics to understand and implement the principles of Industry 5.0 in the evolving industrial landscape.
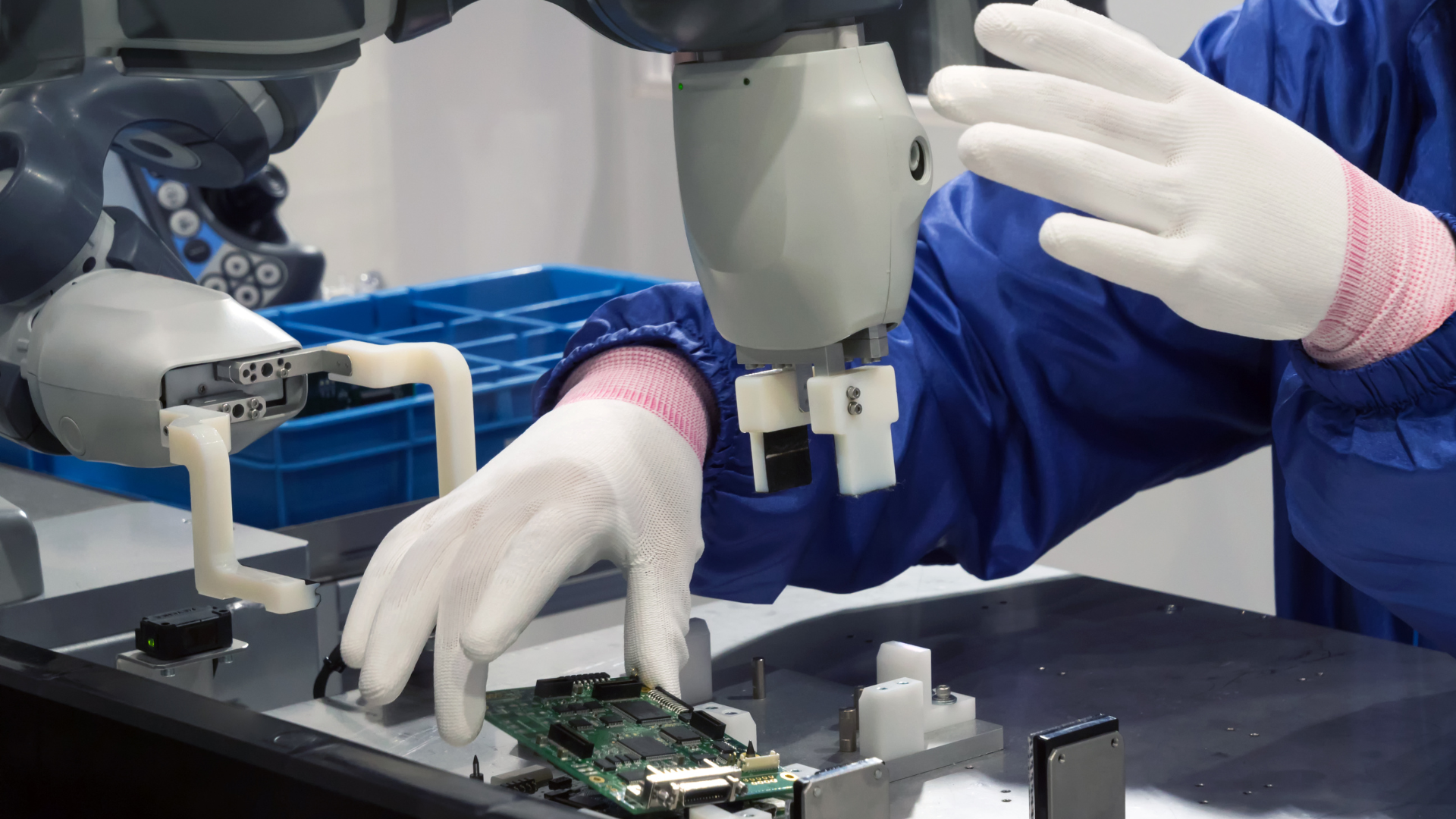

What is Industry 5.0 Mckinsey
Industry 5.0 Mckinsey
Industry 5.0, as analyzed by McKinsey, represents a shift towards a more human-centric approach in manufacturing, where the focus is on enhancing collaboration between humans and smart systems. McKinsey's insights suggest that while Industry 4.0 optimized operations through automation and data analytics, Industry 5.0 seeks to integrate human creativity and decision-making with these advanced technologies. This new phase aims to leverage the strengths of both humans and machines, fostering innovation and improving efficiency in a way that is sustainable and adaptable to future challenges.
Industry 5.0 Research Paper
In a fresh take on Industry 5.0, a recent study breaks down its core, blending insights from both industrial and academic spheres. It highlights the symbiosis between human creativity and machine precision as the hallmark of this new era. The research doesn't gloss over the hurdles, presenting a realistic view of the challenges ahead. Yet, it ends on a note of optimism, pointing toward future directions where human-machine collaboration could redefine manufacturing's landscape.

What is the Industry 4.0 PDF
Industry 4.0 revolutionizes the manufacturing landscape by introducing smart manufacturing concepts and the development of intelligent factories. This shift is marked by the integration of advanced digital technologies like IoT, AI, robotics, and big data analytics, enabling factories to operate more autonomously and efficiently. The primary goal is to significantly boost productivity, efficiency, and flexibility in production processes. Moreover, Industry 4.0 fosters smarter decision-making and enhances the ability to tailor products and operations, meeting the growing demand for customization. This transformation not only optimizes manufacturing and supply chain operations but also adapts to changing market demands, ensuring resilience and sustainability in the industrial sector.
Industrial Revolution 1.0 to 4.0 PPT
The Industrial Revolutions trace the remarkable journey of technological and industrial advancement from the 18th century to the present. Beginning with Industry 1.0, which introduced mechanization via steam power, the narrative progresses to Industry 2.0, where electricity powered mass production. The digital age dawned with Industry 3.0, bringing computers and automation to the forefront, which set the stage for Industry 4.0, where advanced digital technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics are integrated into manufacturing. Each revolution has not only transformed how industries operate but also significantly impacted societal structures and economic paradigms, paving the way for future innovations.
Industry 4.0 Technologies Examples
Internet of Things
Connects and allows communication between devices and machinery, enhancing real-time data exchange and monitoring.
What are the 5 Industrial Revolutions
Industrial revolutions arise from breakthroughs in technology and innovation, catalyzing profound changes in economies and societies. They signal shifts toward greater efficiency and productivity, reflecting humanity's ongoing quest to leverage technology for improved living standards and economic growth.
Industry 5.0 PPT
Industry 5.0 represents an evolution beyond the fourth industrial revolution, emphasizing human collaboration with advanced technologies like AI and robotics to enhance workplace processes. This phase is not solely focused on manufacturing but extends to various sectors, prioritizing human well-being and sustainability alongside productivity and efficiency. The European Union describes it as a shift towards valuing societal and environmental well-being, moving beyond mere economic gains. Industry 5.0 encourages a holistic approach, integrating technological advancements to benefit people, society, and the planet, marking a departure from the profit-centric focus of previous industrial phases.
1st Industrial Revolution:
Began in the 18th century with steam power and mechanization. Mechanized spinning wheels increased thread production, and steam engines replaced muscle power, enhancing productivity. Innovations like the steamship and locomotive revolutionized transportation, enabling longer-distance travel and goods movement.
2nd Industrial Revolution:
Started in the 19th century, marked by electricity and assembly line production. Inspired by conveyor belt systems in slaughterhouses, Henry Ford applied similar principles to automobile manufacturing, drastically improving efficiency and reducing costs with specialized, step-by-step production processes.
3rd Industrial Revolution:
Emerged in the 1970s with the advent of computers and programmable controls, allowing full production automation. Robots and computerized systems could operate independently of human intervention, performing complex manufacturing tasks.
4th Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0):
Current phase, characterized by the integration of information and communication technologies into manufacturing. Building on the third revolution, it introduces interconnected and intelligent systems, enabling smart factories where machines, systems, and humans communicate seamlessly. This revolution enhances automation, predictive maintenance, and efficient, flexible working environments, transforming how products are made, serviced, and improved
What is the Difference Between the 4th and 5th Industrial Revolution
4th Industrial Revolution: Centers on the integration of digital technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics into manufacturing, creating smart factories where machines communicate and operate autonomously to boost efficiency and productivity. It emphasizes the use of big data analytics to optimize operations, enhance decision-making, and improve supply chain efficiencies. This revolution marks a shift towards cyber-physical systems, enabling real-time monitoring and self-optimization of production processes. It also opens avenues for customization and flexibility in manufacturing, catering to unique customer demands through advanced technologies.
5th Industrial Revolution: Builds on Industry 4.0's technological foundation, adding a human-centric approach that fosters collaboration between workers and intelligent systems, aiming to enhance creativity, ensure sustainability, and achieve greater societal value alongside technological advancements. This revolution emphasizes the integration of human intuition and expertise with advanced analytics and machine learning, creating a symbiotic workspace where personalized production and innovation flourish. It prioritizes environmental stewardship and ethical considerations, striving for a balance between economic growth and ecological and social well-being. Industry 5.0 also champions the concept of resilience, preparing industries to adapt swiftly and effectively to future challenges and global changes.
Industry 5.0 Healthcare
Industry 5.0's impact on healthcare is transformative, emphasizing personalized patient care through the integration of advanced technologies with human touch. It leverages AI, robotics, and data analytics to enhance diagnosis, treatment, and patient interaction, while maintaining a core focus on empathy and human-centered care. This approach fosters a healthcare environment where technology and human professionals collaborate to deliver more accurate, efficient, and compassionate care, tailored to individual patient needs.
Industry 5.0 in Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, Industry 5.0 represents a significant shift towards more personalized, sustainable, and collaborative manufacturing processes. It integrates advanced technologies like AI, robotics, and IoT with human ingenuity to create vehicles that are not only efficient and high-tech but also customized to individual preferences. This new industrial phase emphasizes the coexistence of humans and machines on the production line, fostering innovation and efficiency while also prioritizing environmental responsibility and worker well-being in the creation of next-generation vehicles.
Industry 5.0 Advantages and Disadvantages
Industry 5.0 introduces several advantages, including enhanced collaboration between humans and machines, leading to increased innovation and productivity. It fosters personalized and sustainable manufacturing processes, catering to individual customer needs while prioritizing environmental responsibility. However, this shift also brings challenges, such as potential job displacement due to automation and the need for upskilling the workforce to adapt to evolving technological demands. Additionally, there may be concerns regarding data privacy and cybersecurity risks associated with the integration of advanced technologies into industrial processes. Balancing these advantages and disadvantages is crucial for successful implementation and sustainable growth in Industry 5.0.